The KAPA EvoPrep Kits represent Roche’s latest advancements in high-performance, streamlined, and automation-friendly library preparation research solutions. These kits have been validated using a variety of challenging sample inputs, including cell-free DNA, FFPET DNA, and mechanically sheared DNA, and are designed to streamline and reduce workflow steps. The kits feature ReadyMix reagents, available in both tube and plate formats, to facilitate automation. The KAPA EvoT4 DNA Ligase within the ligation ReadyMix of the kits is an evolved potent ligase that is specifically engineered to increase library conversion rates.
Features and benefits of KAPA EvoPrep Kits*
Improved sensitivity, specificity, and ligation efficiency with the addition of our new evolved KAPA EvoT4 DNA ligase, in the kit’s ligation ReadyMix.
- Excellent sequencing performance to support both germline and somatic research applications from challenging sample types such as cfDNA*
- Ligation time of just 5 minutes, shortening workflow duration without compromising results
- Analyze more samples with a wide range of DNA inputs (0.1 ng – 500 ng)
- PCR-free workflows starting from 50 ng of DNA input
- Capture more unique input molecules with high yields and high conversion rates of up to 100%**
- Streamlined and convenient workflows with REACH-compliant*** reagents
- Enhanced flexibility with an 18-month shelf life and better automatability with stabilized ReadyMixes (up to 20 freeze-thaw cycles)
- Validated with the KAPA HyperCap and KAPA HyperPETE portfolios to enable accelerated target enrichment workflows
Product highlights
Simplified and streamlined workflows
- Reduces workflow time with fewer reagents (ReadyMix formulations) and minimal manual steps
- Tubes and plated format, offer increased efficiency and convenience
- Manual- and automation-friendly protocol
- Validated with KAPA HyperCap and KAPA HyperPETE Workflows for accelerated target enrichment

Figure 1: The KAPA EvoPrep Workflow
The KAPA EvoPrep Kit simplifies and streamlines sample prep workflows to reduce complexities, risk for errors, and turnaround times.
*KAPA UDI Adapter Kit and KAPA Library Amplification Primer Mixes, KAPA Universal (UMI) Adapter and KAPA UDI Primer Mixes, and KAPA Cleanup Beads sold separately
Exceptional library yields and sequencing quality
- Achieve higher library yields across a range of input DNA and sample type
- Fewer amplification cycles for downstream processing result in lower duplication rates and higher sequence coverage
- Achieve successful library construction with clinically relevant samples and PCR-free workflows (from as little as 50 ng)
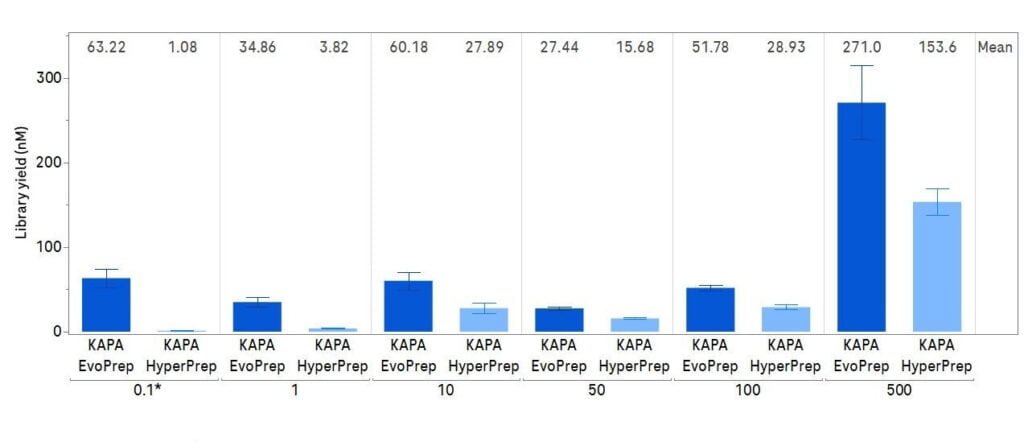
Figure 2: KAPA EvoPrep chemistry enables high library conversion across a range of input DNA
0.1 ng – 500 ng of Covaris-sheared human genomic DNA was used to prepare libraries with KAPA Universal Adapters (with KAPA UDI Primer Mixes) at the recommended adapter: insert molar ratio following the KAPA EvoPrep and KAPA HyperPrep Kit Instructions for Use. Libraries were amplified for various cycles dependent on DNA input to enable visualization. Electropherograms were generated with LabChip GX Touch NGS 3K Assay.*Non-validated input (outside of the input range) for KAPA HyperPrep Kit – optimized cycle number for KAPA EvoPrep Kit inputs used
Optimal utilization of sequencing throughput
- Minimal sequence coverage bias leading to more uniform sequencing coverage and reduced sequencing cost
- Improved sequencing metrics, allowing higher confidence in data due to reduction in sequencing artefacts
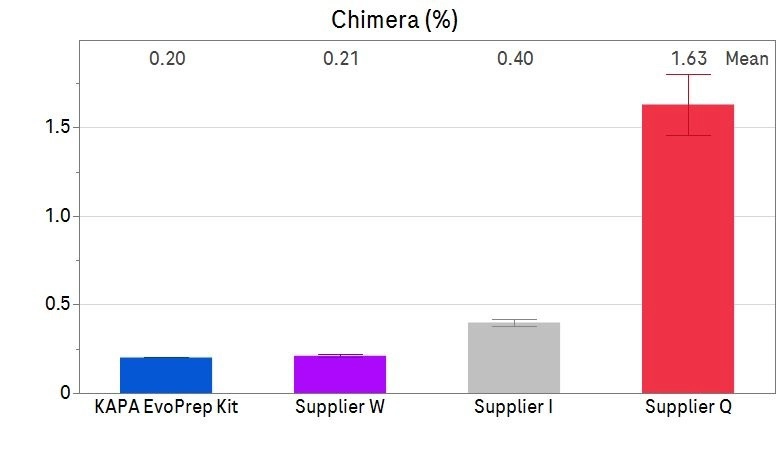
Figure 3: Improved sequencing performance – reduction in Chimeras
PCR-free whole genome libraries were prepared using 100 ng of Covaris-sheared human genomic DNA (NA12878) with the KAPA EvoPrep Kit, Supplier I, Supplier Q and Supplier W, following each supplier’s instructions for use. The KAPA EvoPrep Kit had the lowest percentage of Chimeras present, resulting in higher data confidence* compared to Supplier I, Supplier Q and Supplier W having a higher percentage of Chimeras present.
*Source: Chen, et al. (2024) Characterization and mitigation of artifacts derived from NGS library preparation due to structure-specific sequences in the human genome. BMC Genomics (2024) 25:227 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-024-10157-w
** Dependent on input and sample type
*** Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals